Society
Where’s the best place to live? Prosperity index offers surprises
Reading Time: 3 minutesMany people would probably answer that palm trees and a gleaming beach would be a good start to their idea of earthly paradise. But in real life, the country which scores best on a whole range of economic and quality-of-life issues is a good deal colder.
By Breffni O’Rourke
What’s your idea of the best place in which to live?
Many people would probably answer that palm trees and a gleaming beach would be a good start to their idea of earthly paradise. But in real life, the country which scores best on a whole range of economic and quality-of-life issues is a good deal colder.
It’s Finland.
That’s what the 2009 Prosperity Index issued by the British-based think tank the Legatum Institute finds.
The Legatum Prosperity Index is now in its third year. Its inspiration stems from a speech that onetime U.S. Attorney General Robert Kennedy gave in 1968. He said that the economic indicator most used to measure a country’s progress, namely gross domestic product, or GDP, measures everything "except that which makes life worthwhile."
With this idea as their guiding light, the academics at the Legatum Institute set out to measure human well-being in an infinitely more complex way. They chose nine headings that seemed to sum up the most important ingredients for happiness.
These include, of course, a country’s economic fundamentals, but also personal freedom, health, education, and a safe and supportive society. In addition, there are broad issues, like quality of governance and of domestic institutions, and whether there is space for entrepreneurship and innovation.
William Inboden of the Legatum Institute explains that the list is meant to broaden the thinking of both public and private individuals on the subject of what constitutes progress.
"Certainly it’s targeted at government officials, because a number of factors involved in it relate to government policy, such as respect for human rights, respect for economic freedom and trade freedom and the like," he says. "But also we try to aim this at business leaders, the media, and interested citizens."
One interesting fact shown by the research is that only in the poorest countries does money have an effect on the satisfaction in life. Surprisingly, once a nation rises out of extreme poverty, increases in income play a decreasing role in happiness.
It also shows that many factors leading to prosperity are interdependent. For instance, where economic policies favor small business and innovation, these in turn help to build a broad base of economic stability.
Sound governance is also a key ingredient to prosperity, the report says. Individuals, not governments, are the builders of wealth and happiness. Yet governance is indispensable. Countries in which sound governance leads to satisfied citizens are also most likely to have the best economic fundamentals and the most entrepreneurial societies.
"Our working theory of prosperity is that it’s the responsibility of governments to have wise policies, but also it’s for the citizens to take control of their lives and seize the opportunities when they can," Inboden says.
Under the heading "History Is Not Destiny," the survey points out encouragingly that the highly ranked nations include not only those with a long history of productive economies. There are also those which a couple of decades ago were afflicted with poverty, oppression, and unhappiness.
For instance, Ireland, an economic disaster zone a generation ago, today occupies 11th place in the list of 104 nations.
Similarly, in one generation, Singapore, Taiwan, and South Korea have risen from nowhere to be star economies.
Back in Europe, nations such as Croatia, Estonia, the Czech Republic, Hungary, and Slovakia have emerged from communism and now score comparatively well in the prosperity index.
Croatia, for instance, occupies 35th place out of 104. Despite involvement in a crippling war in the 1990s, it manages today to achieve an "average" rating across the various headings with no weak points and even a "strong" performance in personal freedoms.
Fellow Balkan state Macedonia comes in at No. 59, with weaknesses in its economic fundamentals and personal freedoms.
Iran is relegated to a position — No. 95 — near the end of the index, with failings in most categories, comprising economic fundamentals, democratic institutions, security and safety, governance, personal freedoms, and social trust. It achieves an average rating only in entrepreneurship, education, and health.
Uzbekistan does little better, occupying 92nd place, having the same number of faults as Iran, with a slightly differently spread. Failures are in education, democratic institutions, entrepreneurship, governance, personal freedoms, and social trust.
Kazakhstan, the largest of the Central Asian states, comes in somewhat better at No. 76, with similar failings, but lightened by an "average" score in entrepreneurship and innovation, and in economic fundamentals.
Russia is in 69th place, with one "strong" category, namely education, and five weaknesses, comprising domestic institutions, safety and security, governance, personal freedoms, and social trust.
In Eastern Europe, Ukraine is in 61st place, with weaknesses only in governance and social trust.
Belarus is further down, in 85th place, with its score evenly divided into "average" and "weak," the latter being the usual ones of governance, personal freedoms and social trust, plus entrepreneurship and domestic institutions.
Moldova lies between Russia and Belarus, in 78th place, with all the expected failings.
THE TOP 10
1. Finland
2. Switzerland
3. Sweden
4. Denmark
5. Norway
6. Australia
7. Canada
8. Netherlands
9. United States
10. New Zealand
THE BOTTOM 10
95. Kenya
96. Algeria
97. Tanzania
98. Nigeria
99. Pakistan
100. Cameroon
101. Central African Republic
102. Yemen
103. Sudan
104. Zimbabwe
Society
“They are not needy, but they need help”. How Moldovan volunteers try to create a safe environment for the Ukrainian refugees
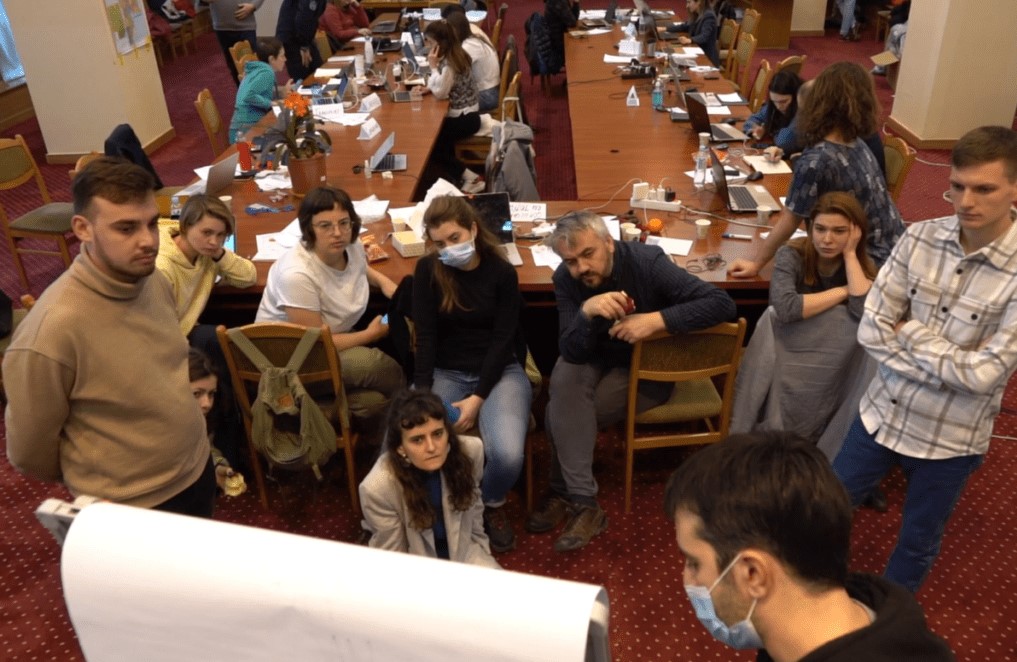

At the Government’s ground floor, the phones ring constantly, the laptop screens never reach standby. In one corner of the room there is a logistics planning meeting, someone has a call on Zoom with partners and donors, someone else finally managed to take a cookie and make some coffee. Everyone is exhausted and have sleepy red eyes, but the volunteers still have a lot of energy and dedication to help in creating a safe place for the Ukrainian refugees.
“It’s like a continuous bustle just so you won’t read the news. You get home sometimes and you don’t have time for news, and that somehow helps. It’s a kind of solidarity and mutual support,” says Vlada Ciobanu, volunteer responsible for communication and fundraising.
The volunteers group was formed from the very first day of war. A Facebook page was created, where all types of messages immediately started to flow: “I offer accommodation”, “I want to help”, “I want to get involved”, “Where can I bring the products?”, “I have a car and I can go to the customs”. Soon, the authorities also started asking for volunteers’ support. Now they all work together, coordinate activities and try to find solutions to the most difficult problems.
Is accommodation needed for 10, 200 or 800 people? Do you need transportation to the customs? Does anyone want to deliver 3 tons of apples and does not know where? Do you need medicine or mobile toilets? All these questions require prompt answers and actions. Blankets, sheets, diapers, hygiene products, food, clothes – people bring everything, and someone needs to quickly find ways of delivering them to those who need them.
Sometimes this collaboration is difficult, involves a lot of bureaucracy, and it can be difficult to get answers on time. “Republic of Moldova has never faced such a large influx of refugees and, probably because nobody thought this could happen, a mechanism of this kind of crisis has not been developed. Due to the absence of such a mechanism that the state should have created, we, the volunteers, intervened and tried to help in a practical way for the spontaneous and on the sport solutions of the problems,” mentions Ecaterina Luțișina, volunteer responsible for the refugees’ accommodation.
Ana Maria Popa, one of the founders of the group “Help Ukrainians in Moldova/SOS Українці Молдовa” says that the toughest thing is to find time and have a clear mind in managing different procedures, although things still happen somehow naturally. Everyone is ready to intervene and help, to take on more responsibilities and to act immediately when needed. The biggest challenges arise when it is necessary to accommodate large families, people with special needs, for which alternative solutions must be identified.
Goods and donations
The volunteers try to cope with the high flow of requests for both accommodation and products of all kinds. “It came to me as a shock and a panic when I found out that both mothers who are now in Ukraine, as well as those who found refuge in our country are losing their milk because of stress. We are trying to fill an enormous need for milk powder, for which the demand is high and the stocks are decreasing”, says Steliana, the volunteer responsible for the distribution of goods from the donation centers.
Several centers have been set up to collect donations in all regions of Chisinau, and volunteers are redirecting the goods to where the refugees are. A system for processing and monitoring donations has already been established, while the volunteer drivers take over the order only according to a unique code.
Volunteers from the collection centers also do the inventory – the donated goods and the distributed goods. The rest is transported to Vatra deposit, from where it is distributed to the placement centers where more than 50 refugees are housed.
When they want to donate goods, but they don’t know what would be needed, people are urged to put themselves in the position of refugees and ask themselves what would they need most if they wake up overnight and have to hurriedly pack their bags and run away. Steliana wants to emphasise that “these people are not needy, but these people need help. They did not choose to end up in this situation.”
Furthermore, the volunteer Cristina Sîrbu seeks to identify producers and negotiate prices for products needed by refugees, thus mediating the procurement process for NGOs with which she collaborates, such as Caritas, World Children’s Fund, Polish Solidarity Fund, Lifting hands, Peace Corps and others.
One of the challenges she is facing now is the identifying a mattress manufacturer in the West, because the Moldovan mattress manufacturer that has been helping so far no longer has polyurethane, a raw material usually imported from Russia and Ukraine.
Cristina also needs to find solutions for the needs of the volunteer groups – phones, laptops, gsm connection and internet for a good carrying out of activities.
Hate messages
The most difficult thing for the communication team is to manage the hate messages on the social networks, which started to appear more often. “Even if there is some sort of dissatisfaction from the Ukrainian refugees and those who offer help, we live now in a very diverse society, there are different kind of people, and we act very differently under stress,” said Vlada Ciobanu.
Translation by Cătălina Bîrsanu
Important
#WorldForUkraine – a map that shows the magnitude of the world’s actions against Russian aggression
The international community and volunteers from all over te world have launched #WorldForUkraine as a platform that shows the magnitude of the world’s actions against the Russian aggression. In a digital world – it is an interactive map of public support of Ukrainians under the hashtag #WorldForUkraine – rallies, flash mobs, protests around the world. In the physical dimension – it is your opportunity to take to the streets and declare: “No to Putin’s aggression, no to war.”
„Today, along with the political and military support, emotional connection with the civilized world and truthful information are extremely important for Ukraine. The power to do it is in your hands. Join the #WorldForUkraine project and contribute to the victorious battle against the bloodshed inflicted on Ukraine by the aggression of the Russian Federation”, says the „about the project” section of the platform.
Go to the streets — Tell people — Connect and Unite — Become POWERFUL
Volunteers have launched #WorldForUkraine as a platform that shows the magnitude of the world’s actions against Russian aggression. In digital world – it is an INTERACTIVE MAP of public support of Ukrainians worldforukraine.net under the hashtag #WorldForUkraine – rallies, flash mobs, protests around the world. In the physical dimension – it is your opportunity to take to the streets and declare: “No to Putin’s aggression, no to war.” There you may find information about past and future rallies in your city in support of Ukraine. This is a permanent platform for Ukrainian diaspora and people all over the world concerned about the situation in Ukraine.
So here’s a couple of things you could do yourself to help:
* if there is a political rally in your city, then participate in it and write about it on social media with geolocation and the hashtag #WorldForUkraine
* if there are no rallies nearby, organize one in support of Ukraine yourself, write about it on social media with geolocation adding the hashtag #WorldForUkraine
The map will add information about gathering by #WorldForUkraine AUTOMATICALLY
Your voice now stronger THAN ever
All rallies are already here: https://worldforukraine.net
Important
How is Moldova managing the big influx of Ukrainian refugees? The authorities’ plan, explained
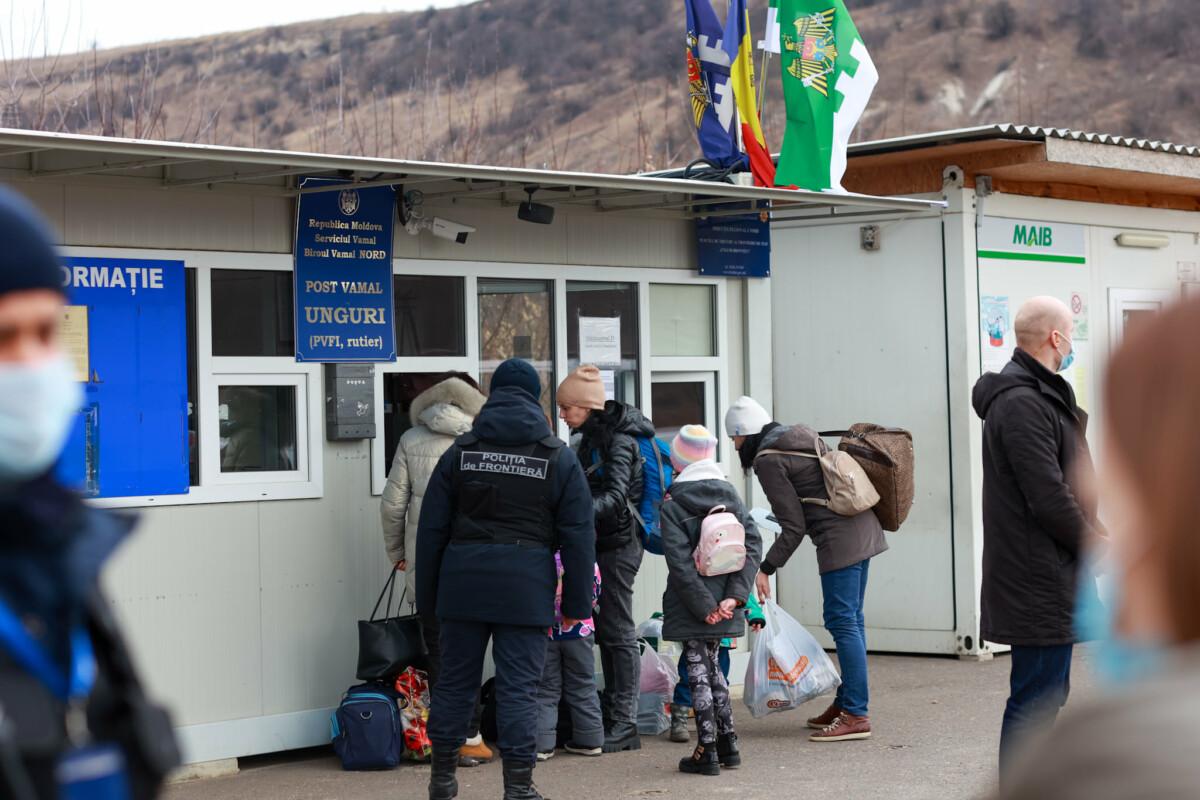

From 24th to 28th of February, 71 359 Ukrainian citizens entered the territory of Republic of Moldova. 33 173 of them left the country. As of this moment, there are 38 186 Ukrainian citizens in Moldova, who have arrived over the past 100 hours.
The Moldovan people and authorities have organized themselves quickly from the first day of war between Russia and Ukraine. However, in the event of a prolonged armed conflict and a continuous influx of Ukrainian refugees, the efforts and donations need to be efficiently managed. Thus, we inquired about Moldova’s long-term plan and the state’s capacity to receive, host, and treat a bigger number of refugees.
On February 26th, the Ministry of Labor and Social Protection of Moldova approved the Regulation of organization and functioning of the temporary Placement Center for refugees and the staffing and expenditure rules. According to the Regulation, the Centers will have the capacity of temporary hosting and feeding at least 20 persons, for a maximum of 3 months, with the possibility of extending this period. The Centers will also offer legal, social, psychological, and primary medical consultations to the refugees. The Center’s activity will be financed from budget allocations, under Article 19 of Provision no. 1 of the Exceptional Situations Commission from February 24th, 2022, and from other sources of funding that do not contravene applicable law.
The Ministry of Inner Affairs and the Government of Moldova facilitated the organization of the volunteers’ group “Moldova for Peace”. Its purpose is to receive, offer assistance and accommodation to the Ukrainian refugees. The group is still working on creating a structure, registering and contacting volunteers, etc. It does not activate under a legal umbrella.
Lilia Nenescu, one of the “Moldova for Peace” volunteers, said that the group consists of over 20 people. Other 1700 registered to volunteer by filling in this form, which is still available. The group consists of several departments:
The volunteers’ department. Its members act as fixers: they’re responsible for connecting the people in need of assistance with the appropriate department. Some of the volunteers are located in the customs points. “The Ministry of Inner Affairs sends us every day the list of the customs points where our assistance is needed, and we mobilize the volunteers”, says Lilia Nenescu.
The Goods Department manages all the goods donated by the Moldavian citizens. The donations are separated into categories: non-perishable foods and non-food supplies. The volunteers of this department sort the goods into packages to be distributed.
The Government intends to collect all the donations in four locations. The National Agency for Food Safety and the National Agency for Public Health will ensure mechanisms to confirm that all the deposited goods comply with safety and quality regulations.
The Service Department operates in 4 directions and needs the volunteer involvement of specialists in psychology, legal assistance (the majority of the refugees only have Ukrainian ID and birth certificates of their children); medical assistance; translation (a part of the refugees are not Ukrainian citizens).
According to Elena Mudrîi, the spokesperson of the Ministry of Health, so far there is no data about the number of Covid-19 positive refugees. She only mentioned two cases that needed outpatient medical assistance: a pregnant woman and the mother of a 4-day-old child.
The Accommodation Department. The volunteers are waiting for the centralized and updated information from the Ministry of Labor about the institutions offering accommodation, besides the houses offered by individuals.
The Transport Department consists of drivers organized in groups. They receive notifications about the number of people who need transportation from the customs points to the asylum centers for refugees.
The municipal authorities of Chișinău announced that the Ukrainian children refugees from the capital city will be enrolled in educational institutions. The authorities also intend to create Day-Care Centers for children, where they will be engaged in educational activities and will receive psychological assistance. Besides, the refugees from the municipal temporary accommodation centers receive individual and group counseling.
In addition to this effort, a group of volunteers consisting of Ana Gurău, Ana Popapa, and Andrei Lutenco developed, with the help of Cristian Coșneanu, the UArefugees platform, synchronized with the responses from this form. On the first day, 943 people offered their help using the form, and 110 people asked for help. According to Anna Gurău, the volunteers communicate with the Government in order to update the platform with the missing data.
Translation from Romanian by Natalia Graur